Introduction
Forge Trinity is a trusted Forged Automotive Components Manufacturer & Supplier for various vehicles. We provide customized and innovative forged parts to enhance the performance and durability of your vehicles. Forging is a process of shaping metal by applying high pressure and temperature using a hammer or a press. Forging can produce parts with high strength, durability, and resistance to wear and fatigue. Forging is widely used in the automotive industry to make components such as engine parts, chassis, bearings, axles, gears, etc.
Benefits of Forged Automotive Components
There are different types of forging processes that can be used for making automotive components, such as:
- Closed die forging: The metal is heated and placed in a die that has a cavity of the desired shape. The metal is then compressed by a hammer or a press until it fills the cavity completely. Closed die forging can produce small and medium-sized parts with high precision and surface finish.
The most common materials used for forging automotive components are steel alloys, such as carbon steel, alloy steel, etc. Steel alloys have high strength, toughness, ductility, and resistance to corrosion and wear. Other materials that can be used for forging include aluminum alloys, titanium alloys, copper alloys, etc.
Forging Processes and Materials
Forging has many benefits for making automotive components, such as:
- Improved mechanical properties: Forging can enhance the strength, hardness, ductility, fatigue resistance, and impact resistance of the metal by aligning its grain structure and eliminating defects.
- Reduced weight: Forging can produce parts with optimal shapes and sizes that reduce the weight of the vehicle and improve its fuel efficiency and performance.
- Lower cost: Forging can reduce the material wastage and machining costs by producing near-net-shape parts that require minimal finishing operations.
- Better quality: Forging can ensure consistent quality and reliability of the parts by eliminating porosity, cracks, voids, etc.
Products
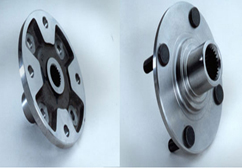
Front Wheel Hubs

Steering Levers

Propeller Shaft Components

Yokes

Rear Wheel Spindles

Powertrain Parts

Material Handling Industry

Radial Piston Motor Cylinder Blocks

Stub Axles

Differential Parts

Pump and Valve Industry

Gear Blanks

Fractured Connecting Rods

Camshafts

Hydraulic Industry


 Advent Developers Pvt. Ltd.
Advent Developers Pvt. Ltd.
